In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses are constantly seeking ways to streamline operations, boost efficiency, and stay ahead of the competition. Enter cloud computing – a revolutionary technology that has transformed the landscape of IT infrastructure and service delivery. This comprehensive guide delves into the cloud computing essentials that unlock a myriad of benefits for organizations of all sizes. From understanding the fundamental concepts to exploring advanced strategies, we’ll navigate through the intricacies of cloud computing, revealing how it can propel your business to new heights. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or a curious entrepreneur, this article will equip you with the knowledge to harness the power of the cloud and drive innovation in your organization.
Contents
Overview: What is Cloud Computing?
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, cloud computing has emerged as a game-changing paradigm. This revolutionary approach to IT infrastructure and service delivery has transformed how businesses operate, innovate, and scale their operations.
Definition and brief history
Cloud computing refers to the on-demand delivery of computing resources—including storage, processing power, and software—over the internet. Rather than maintaining physical servers and data centers, organizations can access these resources from cloud service providers on a pay-as-you-go basis.
The concept of cloud computing can be traced back to the 1960s, but it wasn’t until the late 1990s and early 2000s that it began to take shape as we know it today. The term “cloud computing” was coined in 1996, and major players like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform entered the market in the mid-2000s, catalyzing widespread adoption.
Key characteristics
Cloud computing is characterized by three primary features:
- On-demand self-service: Users can provision computing resources as needed, without requiring human interaction with the service provider.
- Scalability: Resources can be rapidly scaled up or down to meet changing demands, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing: Customers only pay for the resources they use, eliminating the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure.

Benefits of Cloud Computing
Adopting cloud computing unlocks a multitude of advantages for businesses of all sizes. Let’s explore the key benefits:
Cost-effectiveness
One of the most compelling reasons to embrace cloud computing is its potential for significant cost savings. By shifting from a capital expenditure (CapEx) model to an operational expenditure (OpEx) model, businesses can reduce their upfront investments in IT infrastructure. Additionally, the pay-as-you-go pricing structure ensures that organizations only pay for the resources they actually use, optimizing their IT spend.
Scalability and flexibility
Cloud computing provides unparalleled scalability, allowing businesses to rapidly adjust their computing resources based on demand. This elasticity is particularly valuable for companies experiencing seasonal fluctuations or rapid growth. Whether you need to scale up during peak periods or scale down during slower times, cloud services can accommodate your needs without the constraints of physical hardware.
Improved efficiency and productivity
By offloading the management of IT infrastructure to cloud service providers, businesses can focus their resources on core competencies and innovation. Cloud computing enables teams to collaborate more effectively, access data and applications from anywhere, and streamline workflows through automation and integration.
Enhanced data security and disaster recovery
Contrary to common misconceptions, cloud computing can actually enhance data security when implemented correctly. Leading cloud providers invest heavily in state-of-the-art security measures, often surpassing what individual organizations can achieve on their own. Moreover, cloud-based disaster recovery solutions offer robust protection against data loss and system failures, ensuring business continuity in the face of unforeseen events.
Access to advanced technologies
Cloud computing democratizes access to cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics. Small and medium-sized enterprises can now leverage these powerful tools without the need for substantial investments in hardware and expertise.

Types of Cloud Computing
Understanding the different types of cloud environments is crucial for organizations looking to harness the power of cloud computing. Let’s examine the three primary cloud deployment models:
Public cloud
Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party cloud service providers, who deliver computing resources over the internet. These services are available to anyone who wants to use or purchase them, offering a high degree of scalability and cost-effectiveness. Examples of public cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
Private cloud
A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization and can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. This model offers greater control over security and compliance, making it suitable for industries with strict regulatory requirements or organizations with sensitive data.
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid cloud environments combine public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This approach offers the best of both worlds, providing the flexibility and scalability of public clouds while maintaining control over critical assets in a private cloud.
Comparison and use cases
Each cloud deployment model has its strengths and ideal use cases:
- Public cloud: Best for organizations prioritizing cost-effectiveness and scalability, such as startups and companies with fluctuating workloads.
- Private cloud: Ideal for industries with stringent security and compliance requirements, like healthcare and finance.
- Hybrid cloud: Suitable for businesses that need to balance flexibility with control, often used in scenarios where certain workloads must remain on-premises while others can be moved to the public cloud.
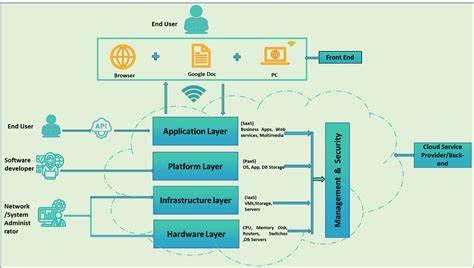
Cloud Computing Essentials
To fully grasp the potential of cloud computing, it’s essential to understand the three primary service models:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users have control over operating systems, storage, and deployed applications, while the cloud provider manages the underlying infrastructure. This model is ideal for organizations that want to avoid investing in and maintaining physical servers and data center infrastructure.
Example: Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS delivers a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of maintaining the underlying infrastructure. This model is particularly beneficial for developers, as it streamlines the application development and deployment process.
Example: Google App Engine
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for users to install and run the application on their own computers. This model offers easy access to sophisticated applications without the burden of software maintenance and support.
Example: Salesforce CRM
Examples and benefits
Each service model offers unique benefits:
- IaaS: Provides maximum flexibility and control over IT resources.
- PaaS: Accelerates application development and deployment.
- SaaS: Offers easy access to sophisticated applications without maintenance overhead.

Implementing Cloud Computing
Adopting cloud computing requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a guide to help organizations navigate the implementation process:
Choosing the right cloud provider
Selecting the appropriate cloud provider is crucial for a successful implementation. Consider factors such as:
- Service offerings and compatibility with your existing systems
- Pricing structure and total cost of ownership
- Security and compliance certifications
- Performance and reliability metrics
- Geographic availability of data centers
- Level of support and documentation
Leading cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, but niche providers may offer specialized services for specific industries or use cases.
Migration strategies
When moving to the cloud, organizations can choose from several migration strategies:
- Rehosting (Lift and Shift): Moving applications to the cloud without major changes
- Refactoring: Modifying applications to take better advantage of cloud-native features
- Replatforming: Making minor modifications to applications to benefit from cloud capabilities
- Rebuilding: Completely redesigning applications as cloud-native solutions
The choice of strategy depends on factors such as application complexity, time constraints, and desired cloud benefits.
Security considerations
While cloud computing can enhance security, it’s essential to implement proper safeguards:
- Implement strong access controls and multi-factor authentication
- Encrypt data both in transit and at rest
- Regularly audit and monitor cloud environments
- Ensure compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA)
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan
Best practices for cloud adoption
To maximize the benefits of cloud computing, organizations should:
- Start with a clear strategy and realistic goals
- Conduct a thorough assessment of existing IT infrastructure and applications
- Invest in training and upskilling for IT staff
- Implement proper governance and cost management processes
- Continuously optimize cloud usage and costs

Case Studies
Real-world examples demonstrate how businesses have leveraged cloud computing to drive innovation and growth:
Case Study 1: Netflix
Netflix’s migration to AWS enabled the company to scale its streaming service globally, handling millions of concurrent users while maintaining high performance and reliability. The move to the cloud allowed Netflix to focus on content creation and user experience rather than managing infrastructure.
Case Study 2: Capital One
The financial services giant embraced cloud computing to accelerate its digital transformation. By migrating to AWS, Capital One improved its ability to analyze data, detect fraud, and develop new products faster. The cloud also enhanced the company’s security posture and regulatory compliance.
Case Study 3: Airbnb
Airbnb leveraged cloud computing to scale its platform rapidly during periods of high growth. The flexibility of cloud resources allowed the company to handle traffic spikes during peak travel seasons and expand into new markets without significant infrastructure investments.
These case studies illustrate how cloud computing can drive innovation, improve operational efficiency, and enable rapid scaling across various industries.
Getting Started with Cloud Computing: A Beginner’s Guide
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals operate, offering scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions. If you’re new to cloud computing, this guide will help you understand the basics and take your first steps.
Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet. Instead of owning and maintaining physical infrastructure, you access these resources as a service from a cloud provider.
Types of Cloud Computing
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides fundamental computing resources like servers, storage, and networking.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a cloud-based platform for developers to build, run, and manage applications.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers applications over the internet, eliminating the need for local installation.
Choosing a Cloud Provider
Several major cloud providers offer a variety of services. Some popular options include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): https://aws.amazon.com/
- Microsoft Azure: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us
- Google Cloud Platform: https://cloud.google.com/
Getting Started with Cloud Computing
- Assess Your Needs: Determine your specific requirements, such as storage, processing power, and scalability.
- Choose a Cloud Provider: Select a provider that aligns with your needs and budget.
- Create an Account: Sign up for a cloud account and explore the available services.
- Learn Basic Concepts: Familiarize yourself with cloud terminology, such as instances, virtual machines, and storage buckets.
- Start Small: Begin with a small-scale project to gain experience and confidence.
- Utilize Cloud Resources: Explore the available services, such as compute instances, storage options, and databases.
- Monitor and Optimize: Regularly monitor your cloud usage and optimize your resources to reduce costs.
Tips for Success
- Leverage Cloud Automation: Use tools and scripts to automate tasks and improve efficiency.
- Consider Hybrid Cloud: Combine on-premises and cloud resources to meet specific needs.
- Stay Updated: Keep up with the latest cloud trends and technologies.
By following these steps and leveraging the resources available, you can successfully embark on your cloud computing journey and unlock the benefits of this transformative technology.
Conclusion
Cloud computing essentials have revolutionized the way organizations approach IT infrastructure and service delivery. By understanding the fundamentals, benefits, and challenges of cloud computing, businesses can harness its power to drive innovation, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in today’s digital landscape.
As cloud computing continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest trends and best practices will be crucial for organizations looking to maximize the benefits of this transformative technology. By embracing cloud computing and its vast potential, businesses can position themselves for success in an increasingly interconnected and data-driven world.







Pingback: Cloud Computing Essentials Lumolog - IndieMinter